Preface #
The development of large model technology can be described as “rapidly evolving,” with seemingly groundbreaking advancements happening every day. 🤔
In reality, how effective are these “groundbreaking advancements”? What is their actual value in engineering practice? Ultimately, these questions must be traced back to those “ordinary” classic principles.
It’s certainly a good thing to keep up with the latest developments in large model technology: it helps us understand research directions and broaden our thinking. However, we should not only focus on the ever-evolving top-tier technologies but also pay attention to the underlying, unchanging fundamentals behind them.
This is the significance of taking the time to read textbooks in an era of rapid technological advancement.
This article primarily focuses on the book “Foundation of Large Models” written by Zhejiang University, which is still being continuously updated.
Basics of Language Models #
This is the most commonly taught knowledge in universities today: n-gram based statistical language modeling, RNN-based language models, and Transformer-based language models. Below is a flowchart of the Transformer architecture.
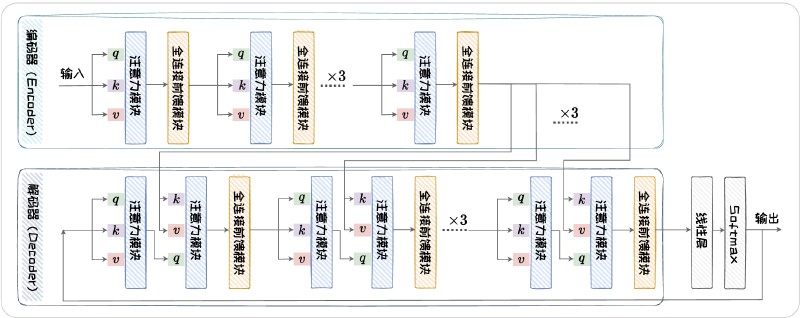
The model architecture doesn’t have much to say, but there are a few interesting questions that were a bit unclear to me before reading the book but became immediately clear afterward.
Q: It’s said that Transformer is a parallel computing architecture, so why can tokens only be generated one after another in a serial manner?
A: The parallel computing of the Transformer is reflected in the processing of known sequences, where all known token vectors are fed into the model in parallel for processing. However, the token generation process remains serial and autoregressive.
Q: Does swapping the order of residual connections and layer normalization affect the model?
A: Networks that place layer normalization after residual connections are called Post-LN, while those that place layer normalization before residual connections are called Pre-LN. Post-LN has a stronger ability to handle representation collapse but is slightly weaker at addressing gradient vanishing, whereas Pre-LN is the opposite.
Q: What does representation collapse mean?
A: During training, the learned representations of the model become less discriminative, meaning different input samples are mapped to similar or even identical feature vectors, causing the model to lose its ability to distinguish between different samples.
Q: Why can the Encoder and Decoder parts of the Transformer be used independently to build a language model?
A:
Q: What loss function is used during the training of Transformer models?
A: Different types of training tasks employ different loss functions. In autoregressive prediction tasks, the loss function is consistent with traditional RNN models, which is the cross-entropy between the model’s predictions and the ground truth.
Q: What are top-k, top-p, and temperature? What are their purposes?
A: Top-k, top-p, and temperature are all parameters used during the decoding process when a language model generates text. However, their meanings are not equivalent—top-k and top-p are sampling methods, while temperature controls the randomness of sampling.
Model decoding can be divided into two approaches: probability maximization, which decodes the text segment with the highest probability, and stochastic sampling, which allows the model to generate more creative text.
In stochastic sampling, different parameters correspond to different sampling methods, namely top-k sampling and top-p sampling. Top-k sampling limits the number of candidate tokens (selecting the top-k highest-probability candidates), while top-p limits the cumulative probability of candidates (selecting candidates whose probabilities sum to at least p). Overall, top-p tends to perform better because it avoids selecting very low-probability tokens, preventing nonsensical outputs, while also enhancing the diversity of generated text, especially when candidate probabilities are relatively balanced.
Temperature adjusts the scale of the input to the softmax function, leveraging its nonlinearity to control sampling randomness. During top-k or top-p sampling, a subset of candidate tokens is selected from the vocabulary, and their probabilities are normalized using the softmax function. The temperature mechanism divides the original probabilities of these candidates by the temperature parameter T. When \( T > 1 \), the differences between candidate probabilities shrink, increasing the model’s randomness, and vice versa.
Large Language Model Architecture #
Scaling Laws #
Scaling Laws reveal how model capabilities evolve with the scale of the model and training data, providing valuable guidance for the design and optimization of large language models.
Widely recognized scaling laws include the Kaplan-McCandlish Scaling Law proposed by OpenAI and the Chinchilla Scaling Law proposed by DeepMind. The latter builds upon the former with further exploration.
$$ L(N,D)=E+\frac{A}{N^\alpha}+\frac{B}{D^\beta} $$$$ E=1.69,A=406.4,B=410.7,\alpha=0.34,\beta=0.28 $$Here, \( L \) represents the cross-entropy loss, \( N \) is the model parameter size, and \( D \) is the training data volume.
Additionally, given a fixed computational budget \( C \), the optimal model and data scales are:
$$ N_{opt}\propto C^{0.46}, D_{opt}\propto C^{0.54} $$